Introduction
The 5G evolution is creating a wealth of new opportunities in the telecom sector. Its core innovative capabilities power some of these opportunities: Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC), and Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC). Capabilities that support connectivity between millions of devices in each square mile can be leveraged to develop advanced use cases and generate new revenue streams.
To date, 166 operators with launched commercial 5G networks across 69 countries/territories worldwide, and 77 operators are investing in 5G standalone[i]. Moreover, by 2025, 5G networks are likely to cover one-third of the world’s population[ii].
While 5G core capabilities and advanced use cases are compelling, deploying this innovative technological shift presents inherent challenges and complexities. Successfully launching and managing a 5G cloud-native network with new core (5GC) and new radio (5G NR) technologies, followed by features such as end-to-end slicing and edge, requires a different mindset.
Operators cannot continue relying on past manual processes and traditional monitoring tools. Adding to this is the operators’ need to guarantee agreed-upon SLAs when supporting use cases for vertical markets, including mission-critical 5G services. As an operator, to meet these innovative requirements, you require a much more intelligent and automated network.
A network that relies on advanced monitoring tools that employ equal levels of innovation at their core functionality. Since, in the end, the success of 5G depends on whether you can manage these networks more efficiently while delivering the promise of a more personalized customer experience.
5G Inherent Challenges
5G Cloud-Native Core
Deploying a cloud-native network is a drastic shift for some operators. Each cloud-native network function (NF) is stateless, completely software-based, and comprised of microservices. Thus, these core NFs can effortlessly be created, deployed, and scaled, facilitating independent life-cycle management.
As a result, operators now need to virtualize hundreds of NFs from the RAN to the network core. NFs that up until recently were proprietary hardware solutions supported by Network Equipment Providers (NEPs) and deployed by network engineers. Moreover, operators now have significant challenges in monitoring these stateless, virtual NFs and troubleshooting network performance in case issues arise to prevent customers’ churn.
5G RAN
5G RAN is a greenfield technology. As many operators choose to virtualize their 5G RAN, they opt for Open RAN (oRAN) or Virtualized RAN (vRAN). Moving to oRAN or vRAN makes access networks more flexible and reduces the cost of managing and maintaining the network. However, this is a greenfield technology for all operators that need to be learned, and the technology needs time to mature.
Furthermore, the deployed 5G RAN uses different spectrum from low to mid and high-band, which is a huge challenge to manage and optimize. While high-band or millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum will significantly enhance the speed and services subscribers receive from a mobile network, another new technology poses new monitoring challenges for operators.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is one of the key 5G service propositions. Built on a single physical infrastructure, each slice is a single, virtual end-to-end network of its own that delivers pre-defined network capabilities designed to serve a specific customer’s business purpose. A network slice can span end-to-end, crossing the RAN, edge, transport, and core.
The ability to visualize, monitor, and assure the quality of services across all these domains is indispensable, yet it presents a significant challenge to operators. To guarantee pre-defined SLAs and ensure the quality of service, you will be required to monitor and analyze traffic performance KQIs and KPIs for each of these virtual slices.
Edge Computing
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) brings cloud resources to the network edge close to applications, connected devices, and end-users, eliminating the journey to the cloud data center. Thus, with edge computing, the data is processed and analyzed closer to its point of origin. Edge computing aims to enhance the user experience by reducing latency and ensuring highly efficient network operation and service delivery.
Yet, the movement to the edge introduces new challenges and issues. To exploit the full power of edge computing, operators’ service offering at the edge needs to meet stringent SLAs of business-specific use cases and applications. Also, as many data transactions are staying at the edge instead of going to data centers, you encounter new challenges in gaining edge visibility to capture the data for analysis and assess network requirements as a whole.
The Critical Role of Automated Assurance
In the past, assurance activities and policies have been mostly manual, time-consuming and reactive. Automating and orchestrating assurance workflows can help realize 5G innovative capabilities, laying the right foundation for operating 5G cloud-native networks.
A recent survey we conducted found that operators chose automation as the top business priority for improving the overall network’s operation. As shown in Figure 1, automation scored almost 40% of respondents’ votes. Automated assurance uses streaming analytics to deliver real-time network intelligence passed on to the operators’ orchestration to detect, analyze, and resolve issues automatically. It also provides end-to-end network troubleshooting from the KPI level down to the session/packet level, critical when rolling out a new network architecture.
Figure 1: As you launch 5G, what is the top business priority for your network quality teams?
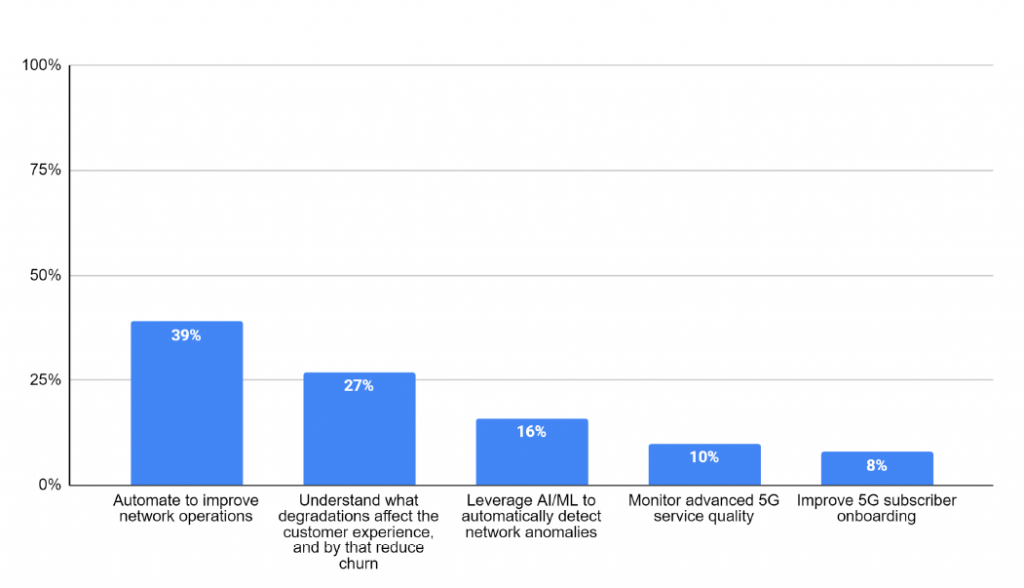
Automated assurance powered by AI and Machine Learning (ML) enables quick and effective validation of network and service performance by analyzing immense amounts of data generated by the network, which no human can do. It can solve complex pattern recognition problems and identify patterns over time and across different data sources, receiving alerts if a certain KPI breach occurs. Thus, it can optimize the network in the most efficient way without manual adaptation, accumulating experience over time.
Deploying automated assurance will help operators overcome 5G inherent complexities by:
- Rapid deployment of change requests related to evolving 5G standards, including automatic testing and verification cycles with CI/CD software development.
- Full monitoring of RAN/vRAN/O-RAN, offering real-time subscriber analytics.
- Visibility into your network slices to ensure SLAs.
- Proactive and continuous monitoring of edge deployments to confirm SLAs.
These assurance solution components can be orchestrated by Kubernetes, which automates the solution for on-demand instantiation, scaling, healing, and updates to ensure services are constantly monitored while being resource-efficient. Hence, operators can optimize their network more efficiently without manual adaptation, accumulating experience over time to a closed-loop approach for network management.
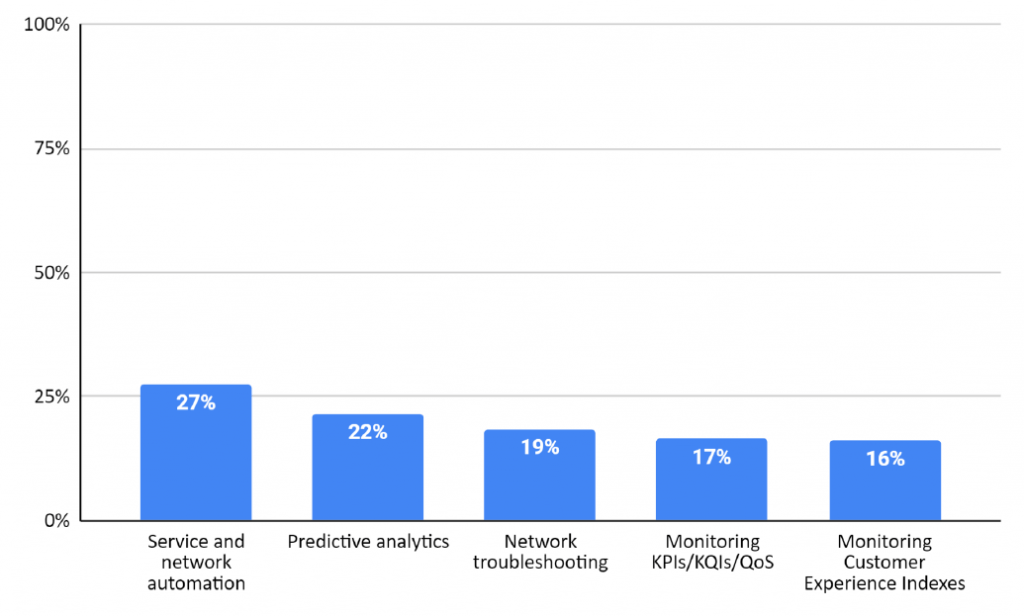
Furthermore, our recent operators’ survey also found that service and network automation have the highest impact on the overall 5G customer experience, as shown in Figure 2. Thus, automated assurance should be the cornerstone of your customers’ experience strategy, enabling you to provide top-level service quality critical to a successful 5G deployment.
Figure 2: Which of the following has the highest impact on customer experience in your 5G network?
Summary
In conclusion, as 5G rollouts continue to gain momentum, operators will be challenged to support their innovative nature and capabilities while delivering new service offerings enabled by advanced technologies, such as slicing and edge computing. To overcome these challenges, operators will need to deploy automated assurance tools to improve operational processes and provide E2E network visibility and monitoring.
RADCOM ACE is our top-tier, automated 5G solution that seamlessly integrates into the 5G core as a Cloud-Native Function (CNF) and provides real-time subscriber analytics and E2E troubleshooting capabilities. Leveraging built-in AI/ML capabilities provides operators with an understanding of the real customer experience and automates the optimization of network quality, saving engineering teams valuable resources.
Being dynamic and fully integrated enables operators to take an on-demand, closed-loop approach to assure a superior customer experience by exceeding expectations for service delivery and problem resolution.
To download our full operators’ survey, click here.
[i] https://gsacom.com/technology/5g/
[ii] https://www.gsma.com/futurenetworks/ip_services/understanding-5g/5g-innovation/
This article is subject to RADCOM’s disclaimers regarding Forward-looking statements and general information under the links below:

