Release 17 of 5G is upon us, bringing some exciting upgrades to the existing 5G standard.
Releases 15 and 16 expand industry-level technological capabilities, and release 17, the third 5G standard, will further enhance system performance and expand into new applications.
With these advancements, 3GPP release 17 will allow for more use cases and features, including:
- Multicast and Broadcast services include public safety services such as mission-critical push-to-talk, over-the-air software updates, live TV, video delivery, and IoT solutions.
- Non-terrestrial networks (NTN) – While having 5G on the moon would be quite an achievement, current use cases can include satellite, air-to-ground, and UAV/drone networks. This also helps with IoT connectivity to and from remote areas, farming, and environmental monitoring. Interestingly, communication between terrestrial and non-terrestrial will improve. Use cases could be slow-moving ships with a limited secondary TN connection and a wide primary NTN connection with a geo satellite connection communicating with a fast-moving plane with a limited primary TN connection and a wide secondary NTN connection via a geo satellite.
- Standalone Non-public networks (SNPN)—Enhancements will allow user equipment (UE) to access an SNPN via external credentials, SNPN onboarding, and support for emergency services.
- Reduced Capability (RedCap), aka NR-Light, is a new tier of User Equipment (UE) devices with longer battery life and a smaller device footprint, optimized for use cases such as wireless industrial sensors, video surveillance, and smart wearables.
- Geo-positioning—Release 17 includes more precise positioning, targeting 20-30cm accuracy in locations indoors and within five meters outdoors.
Other new features include more advanced MIMO, improved capacity, throughput, and battery life, improved edge computing, and support for RRC inactive mode, which is good for low-power devices needing infrequent small data transmissions.
Figure 1 – 3GPP Release 17 Use Cases
Aside from opening new areas of use case development, release 17 also enhances existing 5G capabilities. For example:
- Improvements to latency reduction to enable positioning in time-critical use cases such as remote-control applications
- Provides critical performance indicators to show the reliability and integrity of the measurement report limited to the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) positioning procedure
- Improving spectral efficiency and system capacity, supporting URLLC in unlicensed spectrum environments, and strengthening the framework to support time-sensitive communication (TSC)
- Introduces mechanisms to discover edge application servers
- Release 17 enhancements to Sidelink (SL) operations for 5G New Radio (NR), including reliability, power saving, and coverage enhancements by expanding the scope of NR Sidelink to target V2X, commercial D2D, and public safety.
New Core Network Functions in Release 17
Release 17 defines several new NFs and interfaces, adding more complexity to the 5G Core. Call flows will be more complex than ever, with many new procedures and messages that are potential failure points.
There are at least 18 new NF in release 17. In a recent blog regarding the transition from 4G to 5G, we mentioned that (in Release 16) 5G troubleshooting is approximately 3-5 times more complicated than in legacy 4G or 3G networks. With release 17, 5G monitoring and troubleshooting will be more complex than ever.
The new Release 17 NFs include:
| W-AGF | Wireline Access Gateway Function |
| UCMF | UE Radio Capability Management Function |
| TWIF | Trusted WLAN Interworking Function |
| NSSAAF | Network Slice-Specific Authentication and Authorization Function |
| DCCF | Data Collection Coordination Function |
| MFAF | Messaging Framework Adaptor Function |
| ADRF | Analytical Data Repository Function |
| MTLF and ANLF | NWDAF split into 2 separate network functions: Model training Logical Function and Analytics Logical Function |
| MB-SMF | Multicast Broadcast session management function |
| MB-UPF | Multicast–Broadcast User Plane Function |
| MBSF | Multicast/Broadcast Service Function |
| MBSTF | Multicast/Broadcast Service Transport Function |
| NSACF | Network Slice Access Control Function |
| TSCTSF | Time Sensitive Communication Time Synchronization Function |
| 5G DDNMF | 5G Direct Discovery Name Management Function |
| EASDF | Edge Application Server Discovery Function |
| TSN AF | Time-Sensitive Networking Application Function |
| NSWOF | Non-Seamless WLAN Offload Function |
NWDAF Enhancements
Release 17 provides new network enhancements to the fundamental NWDAF architecture, such as the ability to disaggregate NWDAF into two separate logical entities. This enables multiple NWDAF analytics logical functions (ANLF) in the network to produce analytic reports according to a model distributed from the NWDAF model training logical function (MTLF).
Other new components that are part of the Release 17 Network Analytics framework include:
- DCCF - Data Collection Coordination Function
- MFAF – Messaging Framework Adaptor Function
- ADRF – Analytical Data Repository Function
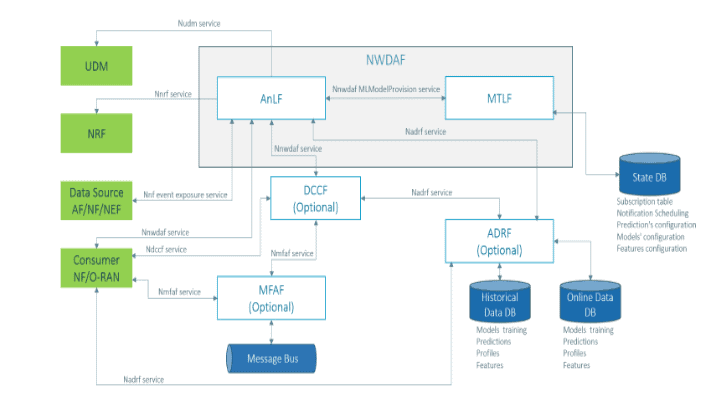
Figure 2 – Release 17 Network Analytics Framework
Service Assurance and Network Insights for Release 17
With the increase in use cases and the enhancement of current offerings, monitoring and analyzing what is happening with your network is vital. Whether it’s edge computing, cloud computing, network slices, or general network maintenance, RADCOM ACE allows you to effectively monitor, detect, and analyze trends and anomalies that provide insightful information for operators to act upon in order to provide the best user experience for their customers.
Summary:
Release 17 enhances current 5G capabilities such as URLLC and the functionality of private networks, as well as providing many new NFs, interfaces, and more complexity to the recent evolution of 5G. As with every technological advancement, network engineers must be able to monitor and troubleshoot network functions and interfaces and ensure their network performance. RADCOM ACE, combined with RADCOM AIM, offers a fully cloud-native automated assurance solution to ensure that operators can quickly and easily understand what is happening within their networks, detect anomalies, and provide ways to optimize their operations and deliver to their end users the best quality of experience possible.
If you have any questions about how release 17 will impact your network and how you can monitor what is happening inside of it, contact us here, and we will be happy to advise on how we can help.
The article is subject to RADCOM’s disclaimers regarding Forward-looking statements and general information under the links below:

