Industrial Digitalization Enabled by Private Networks
Private Mobile Networks (PMNs) are physical or virtual cellular systems that are deployed for private use by enterprises, enabling them to progress digitally and unlock their potential for exponential growth. The demand for private networks based on LTE and increasingly on 5G technologies is expanding with over 500 companies that have been or are currently investing in private networks. Moreover, the number of private LTE/5G networks is projected to reach 14,000 in 2025[i].
According to GSA findings, there are 37 countries/territories with private network deployments based on LTE or 5G. There are also such deployments in various offshore locations serving the oil and gas industries and the shipping industry[ii]. Furthermore, private mobile networks are forecasted to generate over US$64 billion in equipment revenues by 2030[iii].
The Fourth Industrial Revolution (or Industry 4.0) is the ongoing adoption of computers and automation enhanced by smart and autonomous systems which are driven by data and machine learning. When complemented with the transformation of the telecom network to 5G, with low latency and high capacity, industry 4.0 integrates smart technologies such as MIoT (Massive IoT), AR, VR and remote-control capabilities, into manufacturing, utilities, and logistics.
In 5G, a world where everything is always connected with fast speeds and performance, a growing number of enterprise customers are looking to partner with operators to deploy private networks. Private 5G networks serve as an opportunity for potential revenue through which operators can deliver a wide range of enterprise use cases across diverse industry segments.
What are private networks, and why should operators deploy such networks to gain a direct link to enterprises?
Private Networks: A Customer-Specific Functionalities
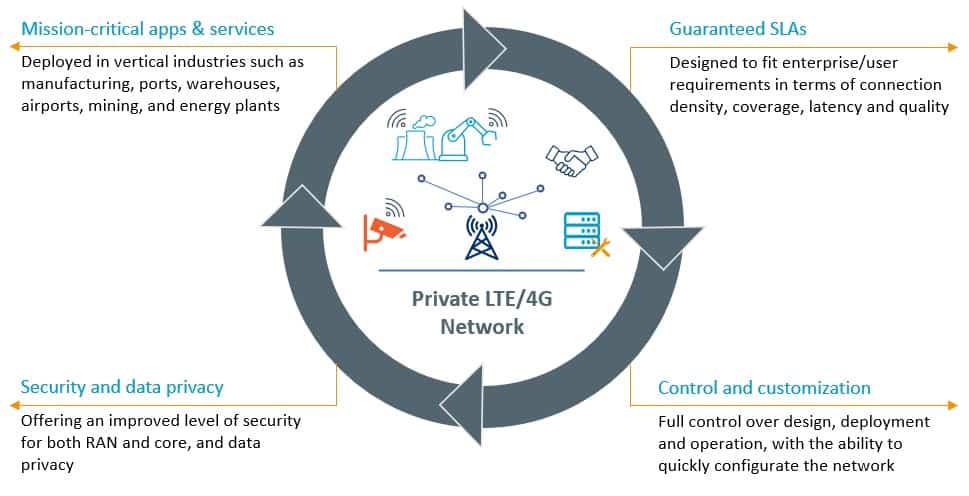
Private networks, also referred to as a Non-Public Network (NPN), are built for the exclusive use of a particular enterprise where all the devices operating on the network are part of a closed network community. Such networks are deployed in a specific location/s to deliver customized functionality in terms of connectivity, coverage, capacity, tailored security, and high quality of service.
Devices registered on public mobile networks won’t work on the private network except when given specific authorization. Thus, a private network is essentially a trusted network in which enterprises pay to receive a committed performance beyond that of a public network with regard to QoS, QoE connectivity, and security.
These fit-for-purpose, high-performing private networks are being widely deployed through many vertical industry sectors such as manufacturing, ports, warehouses, airports, mining, and energy plants. Each of these networks is driving digitalization and leading to the implementation of revolutionized innovative solutions.
As an operator, the projected exponential growth of private LTE/5G networks can lead to additional revenue. When supporting such deployments, you have the opportunity to integrate your own network know-how and management skills to individual enterprises and SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises). With estimates evaluating that between 25% and 40% of SMEs could be served via private mobile networks between 2023 and 2025[iv], this opens up a whole new promising market of customers who are directly working with operators. While each deployment will likely require its own customized functionality and performance attributes, all are aimed at providing a high quality of service to the enterprise end-users.
Private LTE/5G Networks Deployment Options
Private LTE and 5G networks can be deployed according to the following main models:
- A dedicated enterprise network- an enterprise deploys a RAN and core dedicated network built to deliver a pre-defined purpose for its sole use. The enterprise will use its own infrastructure and edge computing assets, combined with dedicated spectrum (in markets where this is permitted).
- Hybrid network- the network deployed is a blend of public and private infrastructure. For example, a slice of the public RAN may be combined with a dedicated on-premises core network.
- Public network slicing- provide a virtualized private network using 5G network slicing over the public network. Thus, an enterprise may obtain most of the advantages of a private network without the costs or complexities of deploying and operating an on-premises network.
Private Networks Require a Management Perspective Shift
When managing the performance of public networks, operators have continuously provided standard functionality, including coverage, connectivity, capacity, and quality of experience. However, they were not required to address mission-critical applications and services, such as: the critical monitoring and control applications in primary production industries including mining, oil extraction, quarrying and refining industries.
Private networks open up a new market where the customer is an enterprise with mission-critical applications and services that require guaranteeing a certain level of performance. As a result, operators will sign a stringent SLA (Service Level Agreement) contract with each enterprise or SME to assure a certain quality of experience.
Service Assurance as a Mission-Critical Component
Deploying private networks for enterprises will require operators to take a different approach to managing their network performance while guaranteeing contracted SLAs, with service assurance becoming a mission-critical component of network architecture. As an operator, you need to integrate an automated assurance solution that runs from the RAN to the core, monitoring, analyzing and predicting network issues to ensure end-users receive a high quality of experience and service delivery meets promised SLAs.
Automated assurance enables the quick and effective validation of network and service performance, isolates network degradations, and proactively pinpoints the root cause. Capabilities include:
- Full visibility into your private networks and their QoS/QoE.
- Advanced troubleshooting and root cause analysis to find and resolve issues quickly.
- Proactive and continuous monitoring of QoE and QoS to confirm SLAs.
- Anticipate service degradations in real-time, setting up alarms to notify if any SLAs are breached.
Summary
In conclusion, private networks are a new and promising revenue stream to operators, offering enterprise customers guaranteed service quality for mission-critical applications and services. Assuring private mobile networks is part of our advanced assurance solution, RADCOM ACE, which enables you to monitor, analyze, and detect degradations in each private network performance in real-time and across all domains. Thus, ensuring that SLAs are met, and enterprise customers can seamlessly run their newly digitized apps and services.
With integrated AI/ML capabilities, RADCOM ACE is able to automate this entire process and predict network issues while assuring a superior customer experience. When integrated into the network, it will enable you to launch and wisely manage private LTE and 5G networks.
To learn more about RADCOM ACE for running a private LTE/5G network, download our white paper about AI Driven-Assurance for 5G.
[i] What are private LTE/5G networks and why are they important? Feb. 2021, Analysys Mason.
[ii] Private Mobile Networks, Jan. 2021, GSA.
[iii] https://www.abiresearch.com/press/private-cellular-networks-generate-over-us64-billion-equipment-revenues-2030/
[iv] https://data.gsmaintelligence.com/research/research/research-2020/radar-june-2020

